Well, what are the reasons for this? What are the symptoms of the disease, its complications, and prevention methods?
The director of the Republic Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Cardiology Consultation Clinic, Oybek Urinov answered these questions.
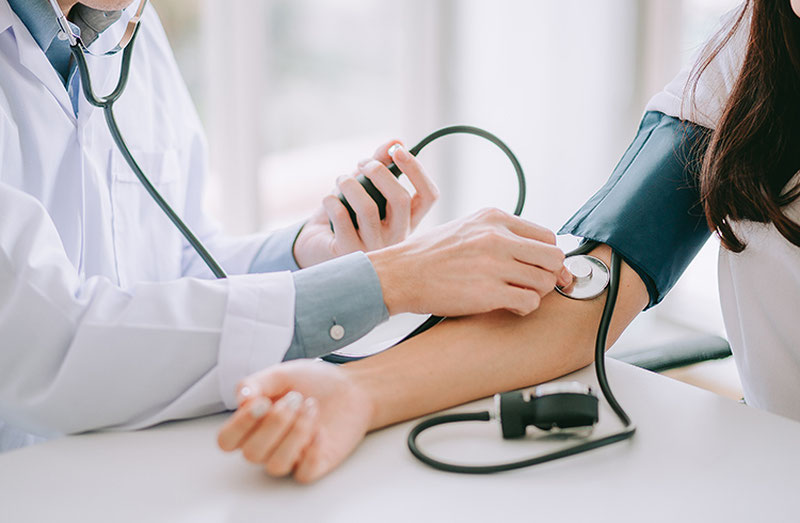
— Hypertension arises as a result of the disruption of the nervous-functional activity of the blood vessels, — says the specialist. — Unfortunately, many people, despite knowing the signs of the illness, postpone treatment. As a result, serious complications occur in the body.
According to the data, hypertension is considered one of the main causes of death in people with cardiovascular diseases.
According to the recommendations, the normal arterial blood pressure should not exceed 140/90 mmHg. If the patient has a resting blood pressure above 140-160/90-95 mmHg during two visits to the doctor, hypertension is diagnosed.
What are the risk factors?
There are several risk factors for the disease. Specifically:
- genetics, age;
- stress;
- high consumption of salty food;
- harmful habits;
- imbalance of fats in the blood and increased sugar levels;
- metabolic syndrome;
- hypodynamia (sedentary lifestyle);
- excess weight, and others.
What are the symptoms?
Patients with high blood pressure experience a number of symptoms, including:
- headache and dizziness, rapid fatigue, nosebleeds;
- noise in the ears;
- impairment of vision and memory;
- nausea and vomiting;
- redness of the skin surface after physical activity;
- strong pressure in the eyes;
- shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, and so on.
If hypertension is not treated in time, it can lead to serious diseases such as myocardial infarction, stroke, chronic heart failure, aneurysm, kidney damage, changes in vision, memory deterioration, and others.
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to engage in physical activity, adhere to a low-salt diet, avoid psychological stress, quit harmful habits, limit animal fats, and undergo preventive medical examinations once a year.